Two-Factor Theory by Frédéric Herzberg (1965)
Frederick Herzberg's two-factor theory (1965) - or theory of 2 motivational factors - states that the motivation of an individual is primarily based upon optimal satisfaction induced by 2 factors:
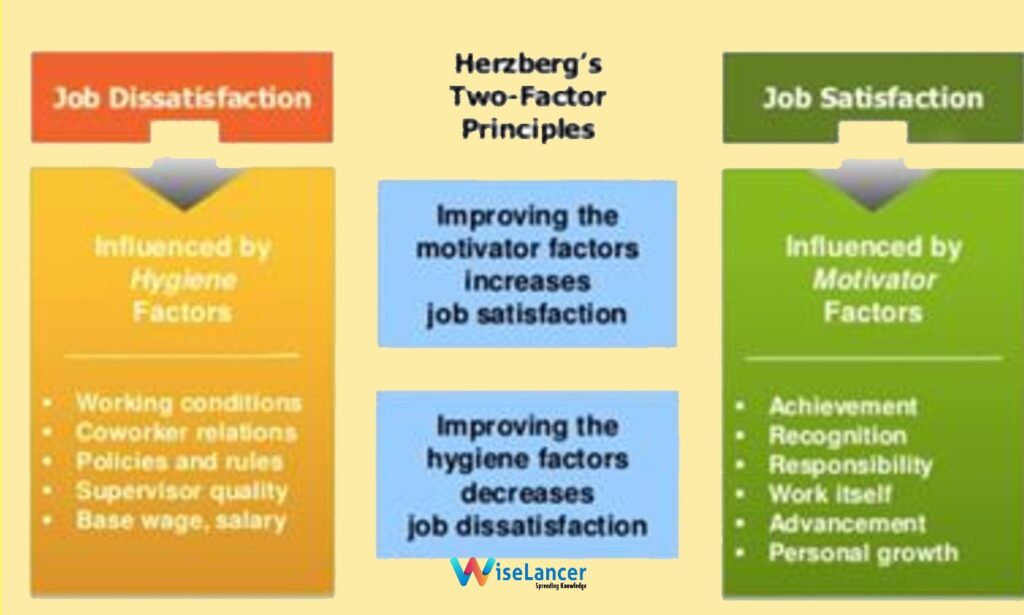
· Hygiene factors – external or physiological: specific to all human beings, they refer in particular to the work environments. This factor can influence dissatisfaction and dissatisfaction. Absence or disappearance of this factor will not be able to generate motivation alone.
· Motor factors – internal or psychological: specific to each person, these factors refer to personal development and are considered to be a source of motivation in case the person does not experience any dissatisfaction at the same time.
According to the Eminent American psychologist
According to this eminent American psychologist in the 1950s, also a management professor, satisfaction and dissatisfaction are neither linked nor opposed. Each of these feelings acts completely independently. This theory, sometimes heavily criticized, has the quality of emphasizing the complexity associated with human nature, especially in terms of motivation (Scheuer, 2000).
Implementing the Herzberg theory in the banking sector, it can be seen that hygiene factors tends to create job satisfaction and not job motivation. However, when motivators are placed, it can develop motivation which can result in improved and higher job performance. For example, provision of hygienic conditions in the workplace will not improve the motivation level of the employee to perform well but, satisfactory working conditions will make employees to continue their job. As a result, hygienic conditions will not have any impact over the performance of the employees. However, on the other side, if the employer is praised or rewarded for their hard work he will be eager to do more thereby, resulting in increased job performance.
For this theory, critics’ state that there is a lot of emphasis over job enrichment whereas, job satisfaction has been completely ignored. Not much important has been given to the pay scale, status as well as interpersonal relationship of the employees which are considered to be general motivators of the employees (Patah et al., 2009).
Two-Factor Theory:
The Two Factor Theory operates a split between the factors which allow avoiding dissatisfaction along with the factors which allow generating satisfaction. As per the Herzberg theory, factors of satisfaction are of no use if those factors which tend to prevent dissatisfaction are not in place. This aspect is clearly visible in Work and Nature of Man.
To be concrete, the first level needs to be reached at in order to not to cause any discontent.
To do this, we must avoid: heat, noise, lack of hygiene and cleanliness, human tensions, the absence of dialogue or communication between the managers and employees as well as job insecurity.
When this first level has been reached, avoiding dissatisfaction is no longer enough but the aim should be to promote satisfaction.
It is now very important to develop as well as put in place those factors that foster motivation and rewards: autonomy, career development, empowerment, encouragement, promotions and even recognition.
Herzberg's bi-factor theory of motivation is primarily based upon an important prerequisite: the person at work seeks first of all to suffer as minimal as possible: after this, he will seek to reduce fatigue or stress to the maximum possible level. The manager must then put in place so-called favorable "hygienic" conditions in the organization so as to avoid employee dissatisfaction (Christopher, 2005).
As has been presented in the pyramid of Maslow, an individual seeks in work a means of accomplishment and fulfillment.
The manager should therefore find ways to stimulate employees while also respecting them as human beings. Such an act can be a complex phenomenon for implementation as it is not merely a question of avoiding dissatisfaction but of setting up conditions favorable to satisfaction.
To be used, for example, for industrial-type companies which encounter difficulties in terms of the social climate or for companies whose working environment is not satisfactory. It is therefore important to show that everything must first be done to avoid dissatisfaction before seeking to promote motivation. A policy of redeveloping the premises of an industrial company can therefore, for example, be a first approach in order to limit and even eliminate job dissatisfaction. Subsequently, other more traditional measures will have to be put in place to allow motivation. It is up to you, thereafter, to propose means to allow an improvement in job satisfaction (Dries, Pepermans and Carlier, 2008).
In my opinion, the theory serves to be a guideline for the managers in structuring employment opportunities so as to include certain factors within jobs that automatically inserts in the factor of satisfaction.
Need Help or Advice in Content Management:
Do you want more advice? Do you have good practices to share? Express yourself in the comments.
Moreover, if you want any help to write content to drive more traffic and boost conversions, get in touch through Contact our team?
Do you want any help writing quality content, driving more traffic to your website, and boosting conversions? You can contact me through my Freelancer.com profile also. I always prefer to work through Freelancer.com for smooth functioning. Here you pay safely and securely.
Read More:
Brand Identity Case Study of Dolce and Gabbana
Successful Project Management Method (Proven)
A STUDY PREDICTING FUTURE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE VS HUMAN BEINGS

Comments are closed.